Australia’s disability sector is expanding rapidly, and so is the need for compassionate, skilled professionals who want to make a real impact in people’s lives. Many aspiring workers begin by asking what a support worker is and how to enter the NDIS workforce confidently. This complete roadmap explains what support workers do, how to become a support worker, the skills and qualifications required, and the long-term career opportunities available. Whether you’re exploring your options or ready to begin your journey, this guide provides everything you need to get started.
What Is a Support Worker?
A support worker is a trained professional who assists individuals to live independently, safely, and with dignity. In the disability sector, this role takes on a specialised form. A disability support worker provides one-on-one assistance with daily living, personal care, social participation, mobility, communication, and emotional well-being.
An NDIS support worker specifically delivers supports funded under the National Disability Insurance Scheme. Unlike general support roles, NDIS support workers tailor their services around individual participant goals, functional needs, and personalised plans. This creates a diverse, flexible, and deeply meaningful profession.
The Role of an NDIS / Disability Support Worker – Duties & Responsibilities

Understanding the support worker responsibilities helps you decide if this career is the right fit. In an NDIS context, support workers play a vital role in empowering participants to achieve their goals while promoting safety and independence.
Key support worker duties include:
- Assisting with personal care such as bathing, grooming, and dressing
- Supporting household tasks including meal preparation and cleaning
- Facilitating community access, social outings, and appointments
- Implementing behaviour support strategies where required
- Strengthening life skills such as budgeting or cooking
- Supporting mobility, transfers, or assistive equipment use
- Monitoring wellbeing and reporting changes
- Documenting progress notes and communicating with teams
- Respecting communication methods, cultural needs, and personal preferences
Having clarity about the duties and responsibilities of support worker roles ensures you’re prepared for the realities of the profession.
Essential Skills & Personal Attributes
Successful NDIS support workers demonstrate both interpersonal strengths and professional capabilities. Essential skills include:
- Effective communication
- Active listening and empathy
- Patience, understanding, and respect
- Cultural competence
- Time management and organisation
- Problem-solving abilities
- Professional boundaries and confidentiality
- Awareness of disability rights and human rights frameworks
These qualities help workers build trust and deliver safe, high-quality supports.
Courses, Certifications & Eligibility
1. Popular Certification Courses
If you want to become a support worker, formal training is one of the strongest ways to gain confidence and credibility. The most recognised qualifications include:
- Certificate III in Individual Support (Disability) – the primary entry-level qualification
- Certificate IV in Disability – suited to those wanting deeper expertise or leadership roles
- Specialised modules, such as mental health support, medication assistance, autism support, or complex care
These certifications are widely accepted by NDIS providers across Australia.
2. Course Eligibility & Prerequisites
Common entry requirements include:
- Minimum secondary education
- Satisfactory English literacy and numeracy levels
- National Police Check and NDIS Worker Screening Check
- Availability for practical work placements (120–160 hours)
- Up-to-date immunisation depending on employer or placement provider
These prerequisites ensure learners are safe, prepared, and compliant.
3. Course Outcomes & Job Readiness
On completion, graduates gain:
- Hands-on disability support experience
- Practical insights from supervised placements
- Understanding of NDIS standards, human rights, and safeguarding
- Skills in communication, documentation, and person-centred practice
- Recognition from employers across the disability sector
These outcomes significantly enhance employability and confidence.
How to Become a Support Worker (Career Roadmap)
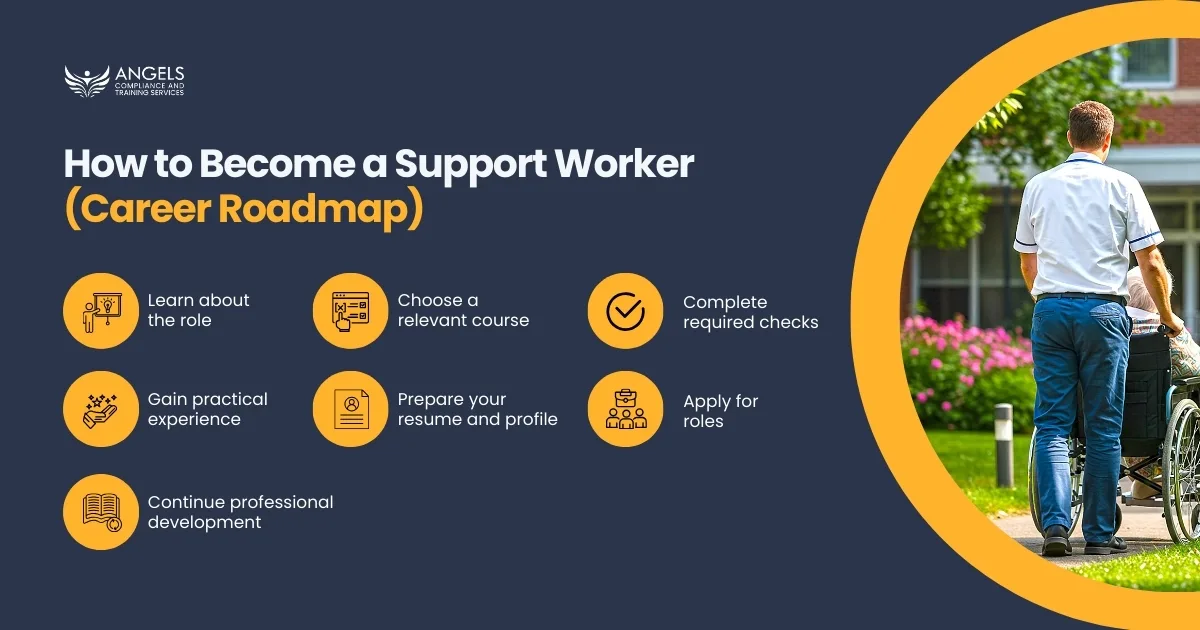
If you’re wondering how I can become a support worker, follow this structured pathway:
- Learn about the role – understand responsibilities and expectations.
- Choose a relevant course – such as Certificate III in Individual Support.
- Complete required checks – including NDIS Worker Screening, police checks, and Working with Children Check (if needed).
- Gain practical experience – through placements, volunteering, or traineeships.
- Prepare your resume and profile – highlight strengths, skills, and certifications.
- Apply for roles – with NDIS providers, community organisations, or as an independent support worker.
- Continue professional development – upskill with additional modules and on-the-job learning.
This roadmap equips you with the knowledge and experience required for long-term success.
Working as an NDIS Support Worker – What to Expect
Support work is a dynamic, rewarding profession that involves meaningful interactions every day. Expect:
- Flexible working hours
- A variety of participant needs and goals
- Opportunities to work in homes, community settings, or group programs
- Emotional and physical demands balanced with personal fulfilment
- Strong teamwork and collaboration with allied health professionals
- A supportive environment driven by participant rights and inclusion
The role is both challenging and deeply rewarding as you help individuals move toward greater independence.
Career Paths for NDIS Support Workers
The disability sector offers extensive long-term career development options.
1. Entry-Level Roles
- Community support worker
- Personal care assistant
2. Mid-Level Roles
- Senior support worker
- Key worker or client liaison
3. Advanced Roles
- Behaviour support practitioner
- Support coordinator
- NDIS plan manager
- Team leader or program manager
4. Lateral Career Options
- Allied health assistant
- Community development roles
- Mental health support
- Nursing or health-related pathways
These pathways allow you to grow your career while staying connected to meaningful, person-centred work.
Duties and Responsibility Pitfalls and Best Practices
Common challenges include unclear boundaries, inconsistent documentation, and a misunderstanding of participant needs. Best practices include:
- Following participant plans and risk assessments
- Maintaining accurate and timely notes
- Using active communication
- Respecting autonomy and encouraging independence
- Upholding professional boundaries
- Seeking supervision or training when unsure
These practices ensure safe, ethical, and high-quality support.
Why Choose This Career? – Benefits & Impact
A career in disability support offers numerous advantages:
- High demand and job security
- Meaningful work that makes a daily difference
- Flexible schedules suitable for various lifestyles
- Opportunities to learn, grow, and specialise
- Deep personal reward and satisfaction
If you value connection, empathy, and purpose-driven work, this career is fulfilling and impactful.
How Angels Compliance & Training Supports Aspiring Disability Support Workers
Beginning a career as a disability support worker can feel complex, especially when navigating training options, compliance requirements, and screening checks. Angels Compliance and Training Services simplifies this process, helping aspiring workers enter the NDIS workforce with confidence and clarity.
a. Access to Role-Specific Training Modules
We offer essential training that equips you with the knowledge and skills required to work safely and professionally, including:
- Infection control and safe practices
- Person-centred support principles
- Mandatory reporting and safeguarding
- Understanding restrictive practices
- Emergency response basics
These modules prepare individuals for real-world support environments.
b. Assistance With Screening Checks
The NDIS requires strict screening processes, and we guide you through each step, including:
- National Police Check
- Working with Children Check (if required)
- ID verification and right-to-work requirements
Our team ensures the process is completed correctly, reducing delays and helping you become job-ready sooner.
c. Compliance Education & Job Readiness
We help you understand:
- Worker responsibilities under NDIS Practice Standards
- Professional boundaries and communication expectations
- Core safety and safeguarding obligations
- Onboarding documentation and compliance essentials
This support helps new workers feel confident and prepared for their first role.
d. Career Pathway Guidance
Our specialist team also assists with:
- Understanding the sector
- Choosing the right certificate courses
- Planning your long-term career pathway
- Navigating early employment steps
With our guidance, the path to becoming a qualified, confident disability support worker becomes clear and achievable.
Conclusion
Becoming an NDIS support worker opens the door to a rewarding, meaningful, and stable career. With the right qualifications, skills, and guidance, you can play a vital role in empowering individuals to live more independently and confidently. If you are ready to begin your journey, explore your training options, or seek professional support, now is the perfect time to take your next step.
